The implementation of a Process API must change.What is a valid approach that minimizes the impact of this change on API clients?
A.
Update the RAML definition of the current Process API and notify API client developers
by sending them links to the updated RAML definition
B.
Postpone changes until API consumers acknowledge they are ready to migrate to a new
Process API or API version
C.
Implement required changes to the Process API implementation so that whenever
possible, the Process API's RAML definition remains unchanged
D.
Implement the Process API changes in a new API implementation, and have the old API
implementation return an HTTP status code 301 - Moved Permanently to inform API clients
they should be calling the new API implementation
Implement required changes to the Process API implementation so that whenever
possible, the Process API's RAML definition remains unchanged
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: Implement required changes to the Process API implementation so that,
whenever possible, the Process API’s RAML definition remains unchanged.
*****************************************
Key requirement in the question is:
>> Approach that minimizes the impact of this change on API clients
Based on above:
>> Updating the RAML definition would possibly impact the API clients if the changes
require any thing mandatory from client side. So, one should try to avoid doing that until
really necessary.
>> Implementing the changes as a completely different API and then redirectly the clients
with 3xx status code is really upsetting design and heavily impacts the API clients.
>> Organisations and IT cannot simply postpone the changes required until all API
consumers acknowledge they are ready to migrate to a new Process API or API version.
This is unrealistic and not possible.
The best way to handle the changes always is to implement required changes to the API
implementations so that, whenever possible, the API’s RAML definition remains
unchanged.
When should idempotency be taken into account?
A. When making requests to update currently locked entities
B. When storing the results of s previous request for use in response to subsequent requests
C. When sending concurrent update requests for the same entity
D. When preventing duplicate processing from multiple sent requests
Which of the below, when used together, makes the IT Operational Model effective?
A.
Create reusable assets, Do marketing on the created assets across organization, Arrange time to time LOB reviews to ensure assets are being consumed or not
B.
Create reusable assets, Make them discoverable so that LOB teams can self-serve and browse the APIs, Get active feedback and usage metrics
C.
Create resuable assets, make them discoverable so that LOB teams can self-serve and browse the APIs
Create resuable assets, make them discoverable so that LOB teams can self-serve and browse the APIs
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: Create reusable assets, Make them discoverable so that LOB teams can self-serve and browse the APIs, Get active feedback and usage metrics.
Diagram, arrow
Description automatically generated
A set of tests must be performed prior to deploying API implementations to a staging
environment. Due to data security and access restrictions, untested APIs cannot be
granted access to the backend systems, so instead mocked data must be used for these
tests. The amount of available mocked data and its contents is sufficient to entirely test the
API implementations with no active connections to the backend systems. What type of
tests should be used to incorporate this mocked data?
A.
Integration tests
B.
Performance tests
C.
Functional tests (Blackbox)
D.
Unit tests (Whitebox)
Unit tests (Whitebox)
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: Unit tests (Whitebox)
*****************************************
Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/3.9/testing-strategies
As per general IT testing practice and MuleSoft recommended practice, Integration and
Performance tests should be done on full end to end setup for right evaluation. Which
means all end systems should be connected while doing the tests. So, these options are
OUT and we are left with Unit Tests and Functional Tests.
As per attached reference documentation from MuleSoft:
Unit Tests - are limited to the code that can be realistically exercised without the need to
run it inside Mule itself. So good candidates are Small pieces of modular code, Sub Flows,
Custom transformers, Custom components, Custom expression evaluators etc.
Functional Tests - are those that most extensively exercise your application configuration.
In these tests, you have the freedom and tools for simulating happy and unhappy paths.
You also have the possibility to create stubs for target services and make them success or
fail to easily simulate happy and unhappy paths respectively.
As the scenario in the question demands for API implementation to be tested before
deployment to Staging and also clearly indicates that there is enough/ sufficient amount of
mock data to test the various components of API implementations with no active
connections to the backend systems, Unit Tests are the one to be used to incorporate this
A company deploys Mule applications with default configurations through Runtime Manager to customer-hosted Mule runtimes. Each Mule application is an API implementation that exposes RESTful interfaces to API clients. The Mule runtimes are managed by the MuleSoft-hosted control plane. The payload is never used by any Logger components. When an API client sends an HTTP request to a customer-hosted Mule application, which metadata or data (payload) is pushed to the MuleSoft-hosted control plane?
A. Only the data
B. No data
C. The data and metadata
D. Only the metadata
Which statement is true about Spike Control policy and Rate Limiting policy?
A. All requests are rejected after the limit is reached in Rate Limiting policy, whereas the requests are queued in Spike Control policy after the limit is reached
B. In a clustered environment, the Rate Limiting.and Spike Control policies are applied to each node in the cluster
C. To protect Experience APIs by limiting resource consumption, Rate Limiting policy must be applied
D. In order to apply Rate Limiting and Spike Control policies, a contract to bind client application and API is needed for both
Refer to the exhibit.
A.
Option A
B.
Option B
C.
Option C
D.
Option D
Option D
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: XML over HTTP
*****************************************
>> API-led connectivity and Application Networks urge to have the APIs on HTTP based
protocols for building most effective APIs and networks on top of them.
>> The HTTP based APIs allow the platform to apply various varities of policies to address
many NFRs
>> The HTTP based APIs also allow to implement many standard and effective
implementation patterns that adhere to HTTP based w3c rules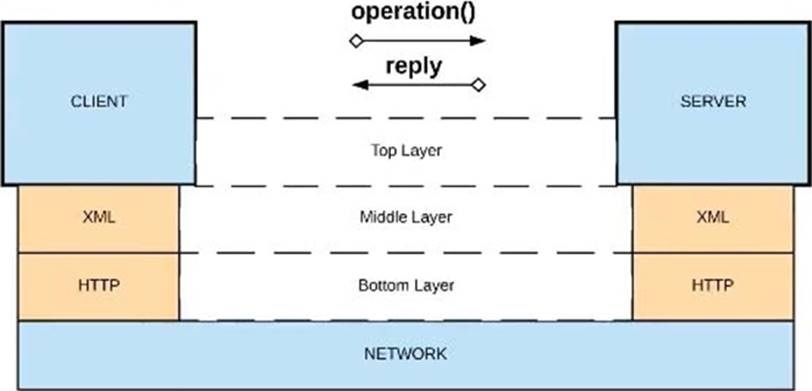
An organization is implementing a Quote of the Day API that caches today's quote.
What scenario can use the GoudHub Object Store via the Object Store connector to persist
the cache's state?
A.
When there are three CloudHub deployments of the API implementation to three
separate CloudHub regions that must share the cache state
B.
When there are two CloudHub deployments of the API implementation by two Anypoint
Platform business groups to the same CloudHub region that must share the cache state
C.
When there is one deployment of the API implementation to CloudHub and anottV
deployment to a customer-hosted Mule runtime that must share the cache state
D.
When there is one CloudHub deployment of the API implementation to three CloudHub
workers that must share the cache state
When there is one CloudHub deployment of the API implementation to three CloudHub
workers that must share the cache state
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: When there is one CloudHub deployment of the API implementation to
three CloudHub workers that must share the cache state.
*****************************************
Key details in the scenario:
>> Use the CloudHub Object Store via the Object Store connector
Considering above details:
>> CloudHub Object Stores have one-to-one relationship with CloudHub Mule Applications.
>> We CANNOT use an application's CloudHub Object Store to be shared among multiple
Mule applications running in different Regions or Business Groups or Customer-hosted
Mule Runtimes by using Object Store connector.
>> If it is really necessary and very badly needed, then Anypoint Platform supports a way
by allowing access to CloudHub Object Store of another application using Object Store
REST API. But NOT using Object Store connector.
So, the only scenario where we can use the CloudHub Object Store via the Object Store
connector to persist the cache’s state is when there is one CloudHub deployment of the
API implementation to multiple CloudHub workers that must share the cache state
| Page 1 out of 19 Pages |