An API with multiple API implementations (Mule applications) is deployed to both CloudHub and customer-hosted Mule runtimes. All the deployments are managed by the MuleSoft-hosted control plane. An alert needs to be triggered whenever an API implementation stops responding to API requests, even if no API clients have called the API implementation for some time. What is the most effective out-of-the-box solution to create these alerts to monitor the API implementations?
A. Create monitors in Anypoint Functional Monitoring for the API implementations, where each monitor repeatedly invokes an API implementation endpoint
B. Add code to each API client to send an Anypoint Platform REST API request to generate a custom alert in Anypoint Platform when an API invocation times out
C. Handle API invocation exceptions within the calling API client and raise an alert from that API client when such an exception is thrown
D. Configure one Worker Not Responding alert.in Anypoint Runtime Manager for all API implementations that will then monitor every API implementation
Explanation:
In scenarios where multiple API implementations are deployed across
different environments (CloudHub and customer-hosted runtimes), Anypoint Functional
Monitoring is the most effective tool to monitor API availability and trigger alerts when an
API implementation becomes unresponsive. Here’s how it works:
An API implementation is updated. When must the RAML definition of the API also be updated?
A.
When the API implementation changes the structure of the request or response messages
B.
When the API implementation changes from interacting with a legacy backend system deployed on-premises to a modern, cloud-based (SaaS) system
C.
When the API implementation is migrated from an older to a newer version of the Mule runtime
D.
When the API implementation is optimized to improve its average response time
When the API implementation changes the structure of the request or response messages
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: When the API implementation changes the structure of the request or
response messages
*****************************************
>> RAML definition usually needs to be touched only when there are changes in the
request/response schemas or in any traits on API.
>> It need not be modified for any internal changes in API implementation like performance
tuning, backend system migrations etc
Refer to the exhibit. An organization is running a Mule standalone runtime and has
configured Active Directory as the Anypoint Platform external Identity Provider. The organization does not have budget for other system components.
What policy should be applied to all instances of APIs in the organization to most
effecuvelyKestrict access to a specific group of internal users?
A.
Apply a basic authentication - LDAP policy; the internal Active Directory will be
configured as the LDAP source for authenticating users
B.
Apply a client ID enforcement policy; the specific group of users will configure their client applications to use their specific client credentials
C.
Apply an IP whitelist policy; only the specific users' workstations will be in the whitelist
D.
Apply an OAuth 2.0 access token enforcement policy; the internal Active Directory will be configured as the OAuth server
Apply a basic authentication - LDAP policy; the internal Active Directory will be
configured as the LDAP source for authenticating users
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: Apply a basic authentication - LDAP policy; the internal Active Directory
will be configured as the LDAP source for authenticating users.
*****************************************
>> IP Whitelisting does NOT fit for this purpose. Moreover, the users workstations may not
necessarily have static IPs in the network.
>> OAuth 2.0 enforcement requires a client provider which isn't in the organizations system
components.
>> It is not an effective approach to let every user create separate client credentials and
configure those for their usage.
The effective way it to apply a basic authentication - LDAP policy and the internal Active
Directory will be configured as the LDAP source for authenticating users.
Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/basic-authentication-ldap-concept
What should be ensured before sharing an API through a public Anypoint Exchange portal?
A.
The visibility level of the API instances of that API that need to be publicly accessible should be set to public visibility
B.
The users needing access to the API should be added to the appropriate role in
Anypoint Platform
C.
The API should be functional with at least an initial implementation deployed and accessible for users to interact with
D.
The API should be secured using one of the supported authentication/authorization mechanisms to ensure that data is not compromised
The visibility level of the API instances of that API that need to be publicly accessible should be set to public visibility
Explanation: Explanation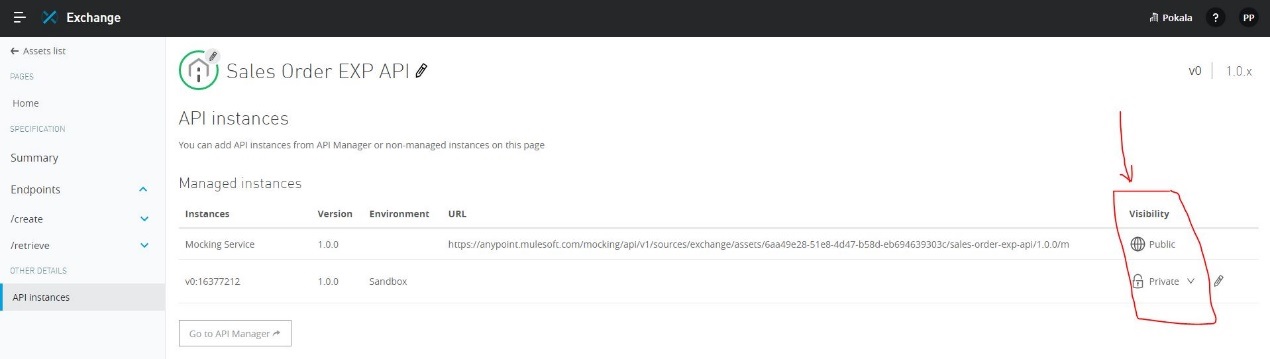
Mule applications that implement a number of REST APIs are deployed to their own subnet
that is inaccessible from outside the organization.
External business-partners need to access these APIs, which are only allowed to be
invoked from a separate subnet dedicated to partners - called Partner-subnet. This subnet
is accessible from the public internet, which allows these external partners to reach it.
Anypoint Platform and Mule runtimes are already deployed in Partner-subnet. These Mule
runtimes can already access the APIs.
What is the most resource-efficient solution to comply with these requirements, while
having the least impact on other applications that are currently using the APIs?
A.
Implement (or generate) an API proxy Mule application for each of the APIs, then deploy the API proxies to the Mule runtimes
B.
Redeploy the API implementations to the same servers running the Mule runtimes
C.
Add an additional endpoint to each API for partner-enablement consumption
D.
Duplicate the APIs as Mule applications, then deploy them to the Mule runtimes
Implement (or generate) an API proxy Mule application for each of the APIs, then deploy the API proxies to the Mule runtimes
What API policy would LEAST likely be applied to a Process API?
A.
Custom circuit breaker
B.
Client ID enforcement
C.
Rate limiting
D.
JSON threat protection
JSON threat protection
Explanation: Explanation
Correct Answer: JSON threat protection
*****************************************
Fact: Technically, there are no restrictions on what policy can be applied in what layer. Any
policy can be applied on any layer API. However, context should also be considered
properly before blindly applying the policies on APIs.
That is why, this question asked for a policy that would LEAST likely be applied to a
Process API.
From the given options:
>> All policies except "JSON threat protection" can be applied without hesitation to the
APIs in Process tier.
>> JSON threat protection policy ideally fits for experience APIs to prevent suspicious
JSON payload coming from external API clients. This covers more of a security aspect by
trying to avoid possibly malicious and harmful JSON payloads from external clients calling
experience APIs.
As external API clients are NEVER allowed to call Process APIs directly and also these
kind of malicious and harmful JSON payloads are always stopped at experience API layer
only using this policy, it is LEAST LIKELY that this same policy is again applied on Process
Layer API.
Which two statements are true about the technology architecture of an Anypoint Virtual
Private Cloud (VPC)?
(Choose 2 answers)
A. Ports 8081 and 8082 are used
B. CIDR blacks are used
C. Anypoint VPC is responsible for load balancing the applications
D. Round-robin load balancing is used to distribute client requests across different applications
E. By default, HTTP requests can be made from the public internet to workers at port 6091
Explanation:
An Anypoint Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) provides a secure and private
networking environment for MuleSoft applications, using specific architectural elements:
What is the most performant out-of-the-box solution in Anypoint Platform to track
transaction state in an asynchronously executing long-running process implemented as a
Mule application deployed to multiple CloudHub workers?
A.
Redis distributed cache
B.
java.util.WeakHashMap
C.
Persistent Object Store
D.
File-based storage
Persistent Object Store
Explanation: Correct Answer: Persistent Object Store
*****************************************
>> Redis distributed cache is performant but NOT out-of-the-box solution in Anypoint
Platform
>> File-storage is neither performant nor out-of-the-box solution in Anypoint Platform
>> java.util.WeakHashMap needs a completely custom implementation of cache from
scratch using Java code and is limited to the JVM where it is running. Which means the
state in the cache is not worker aware when running on multiple workers. This type of
cache is local to the worker. So, this is neither out-of-the-box nor worker-aware among
multiple workers on cloudhub. https://www.baeldung.com/java-weakhashmap
>> Persistent Object Store is an out-of-the-box solution provided by Anypoint Platform
which is performant as well as worker aware among multiple workers running on
CloudHub. https://docs.mulesoft.com/object-store/
So, Persistent Object Store is the right answer.
| Page 1 out of 19 Pages |